UAV
Type of resources
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
-
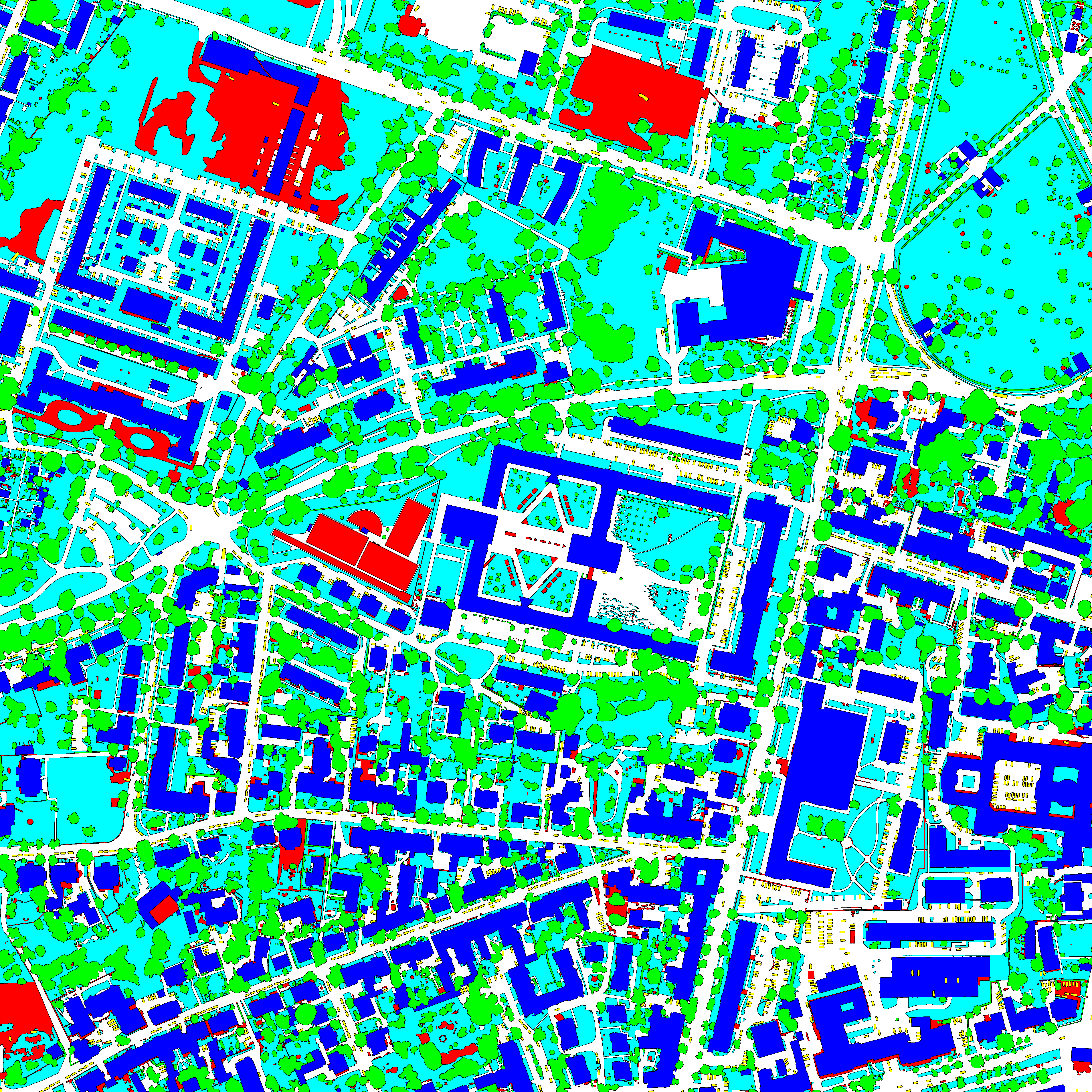
This dataset contains semantic segmentation train-validation-test data splits of (1) the ISPRS Potsdam orthomosaic (https://www.isprs.org/education/benchmarks/UrbanSemLab/2d-sem-label-potsdam.aspx), (2) the RIT-18 landcover orthomosaic (https://github.com/rmkemker/RIT-18), and (3) the industrial environment of the photorealistic Flightmare quadrotor simulator (https://github.com/uzh-rpg/flightmare). All splits are generated by simulating UAV missions at fixed altitudes. We use these datasets in our "An Informative Path Planning Framework for Active Learning in UAV-based Semantic Mapping" paper. Further, it contains (4) model checkpoints of our proposed Bayesian ERFNet framework (https://github.com/dmar-bonn/bayesian_erfnet) pre-trained on Cityscapes, (5) the ISPRS Potsdam and RIT-18 RGB and semantically labelled orthomosaics, and (6) the Flightmare render binary for the industrial environment.
-
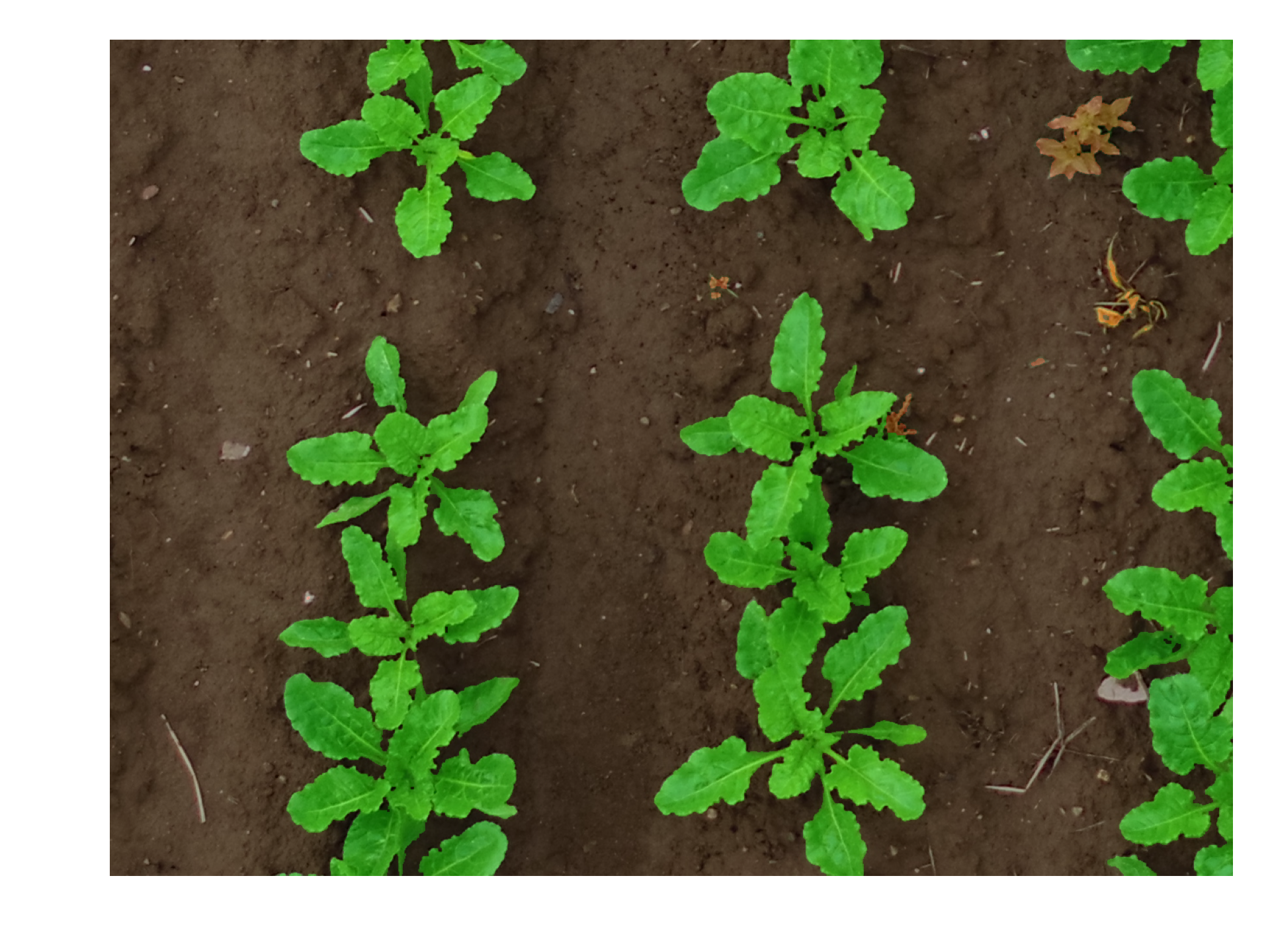

Images captured by an UAV at Bonn with additional annotations of crops and weeds (2017). The *split.yaml* file contains information about which images belong to the train, val, and test set.
-
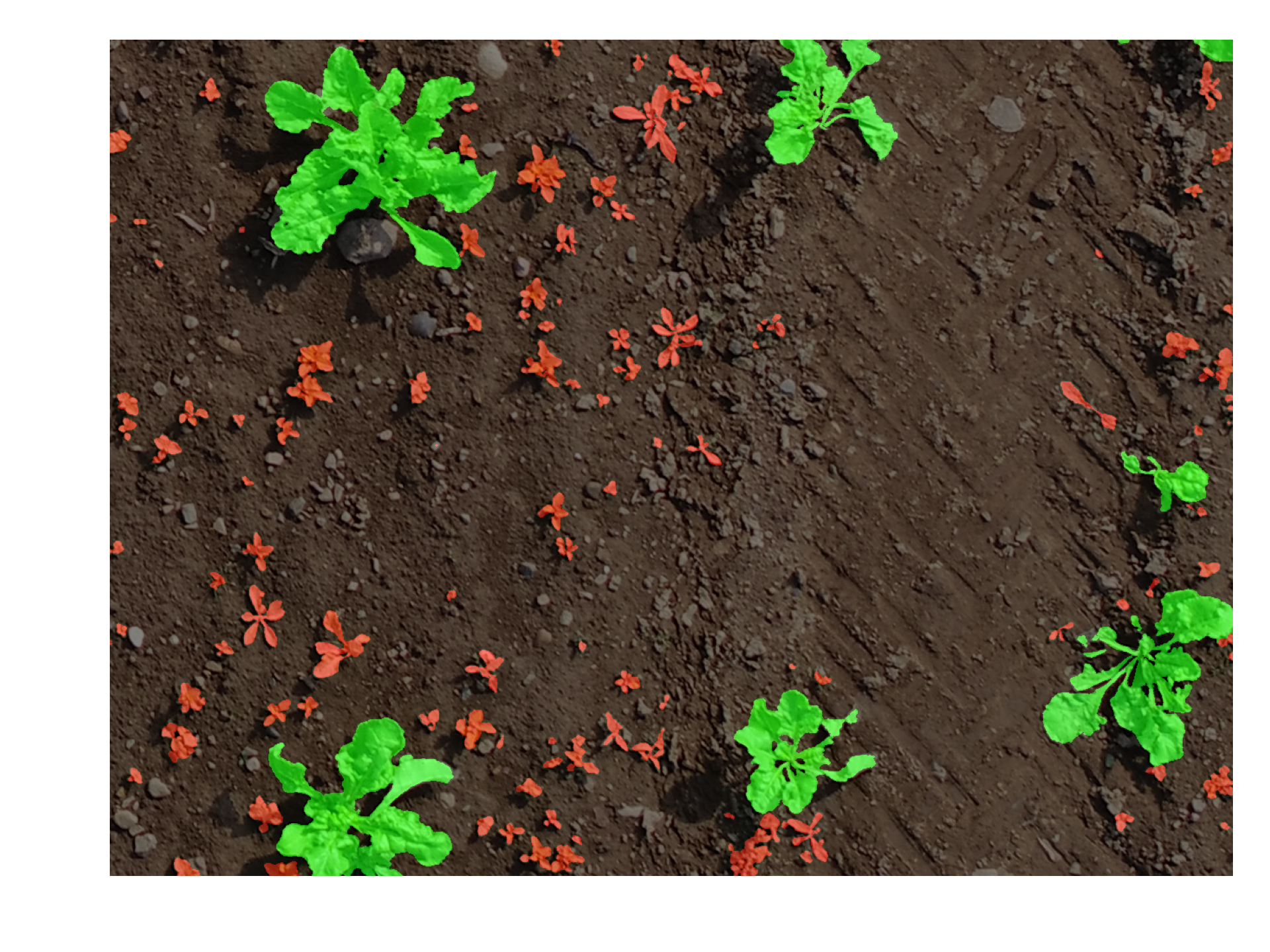
Images captured by an UAV at Zurich with additional annotations of crops and weeds (2017). The *split.yaml* file contains information about which images belong to the train, val, and test set.
-
RGB orthomosaics from PR central experiment at Campus Klein-Altendorf acquired in years 2021 and 2022. Image data was acquired at 20m flight altitude throughout the vegetation season in March-September. Orthomosaics are georeferenced in WGS84 / UTM 32N
-

A Dataset Towards Point Cloud-Based Organ-Level Phenotyping of Sugar Beet Plants Under Real Field Conditions
-
MicaSense Dual 10 channel multispectral reflectance orthomosaics of PhenoRob Central Experiement 2022
-
UAV RGB images captured using PhaseOne. Also included, the process orthophotos and camera extrinsics. Data collected in 2023 at the PhenoRob Central Experiments in CKA.
-
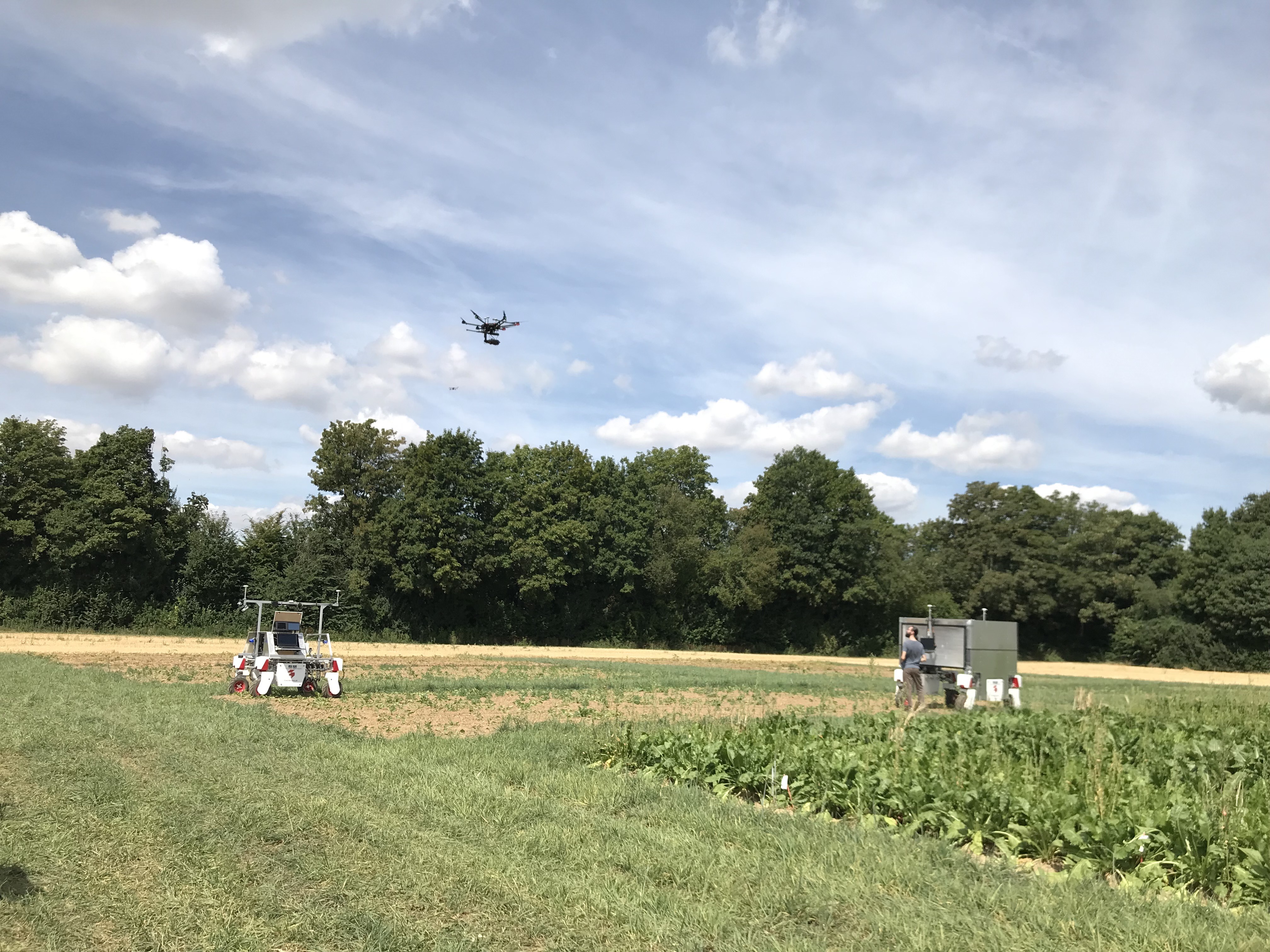

Same field, different sensors and robots.
-
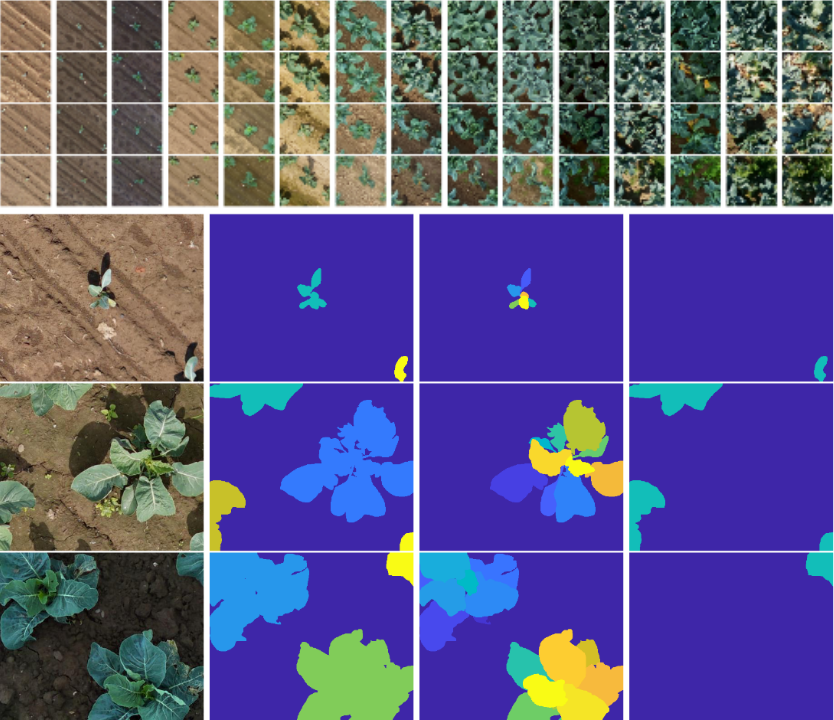

This dataset contains georeferenced, image-based UAV time-series of two monitored cauliflower fields acquired in two years, 2020 and 2021. The proposed dataset contains RGB and multispectral orthophotos with coordinates of approximately 14000 individual cauliflower plants. The coordinates enable extraction of complete and incomplete time-series of image patches showing individual plants. The dataset contains the collected phenotypic traits of 740 plants, including the developmental stage and plant and cauliflower size. The harvestable product is completely covered by leaves, thus, plant IDs and coordinates are provided to extract image pairs of plants pre- and post-defoliation. In addition, to facilitate classification, detection, segmentation, instance segmentation, and other similar computer vision tasks, the proposed dataset contains pixel-accurate leaf and plant instance segmentations, as well as stem annotations.
-
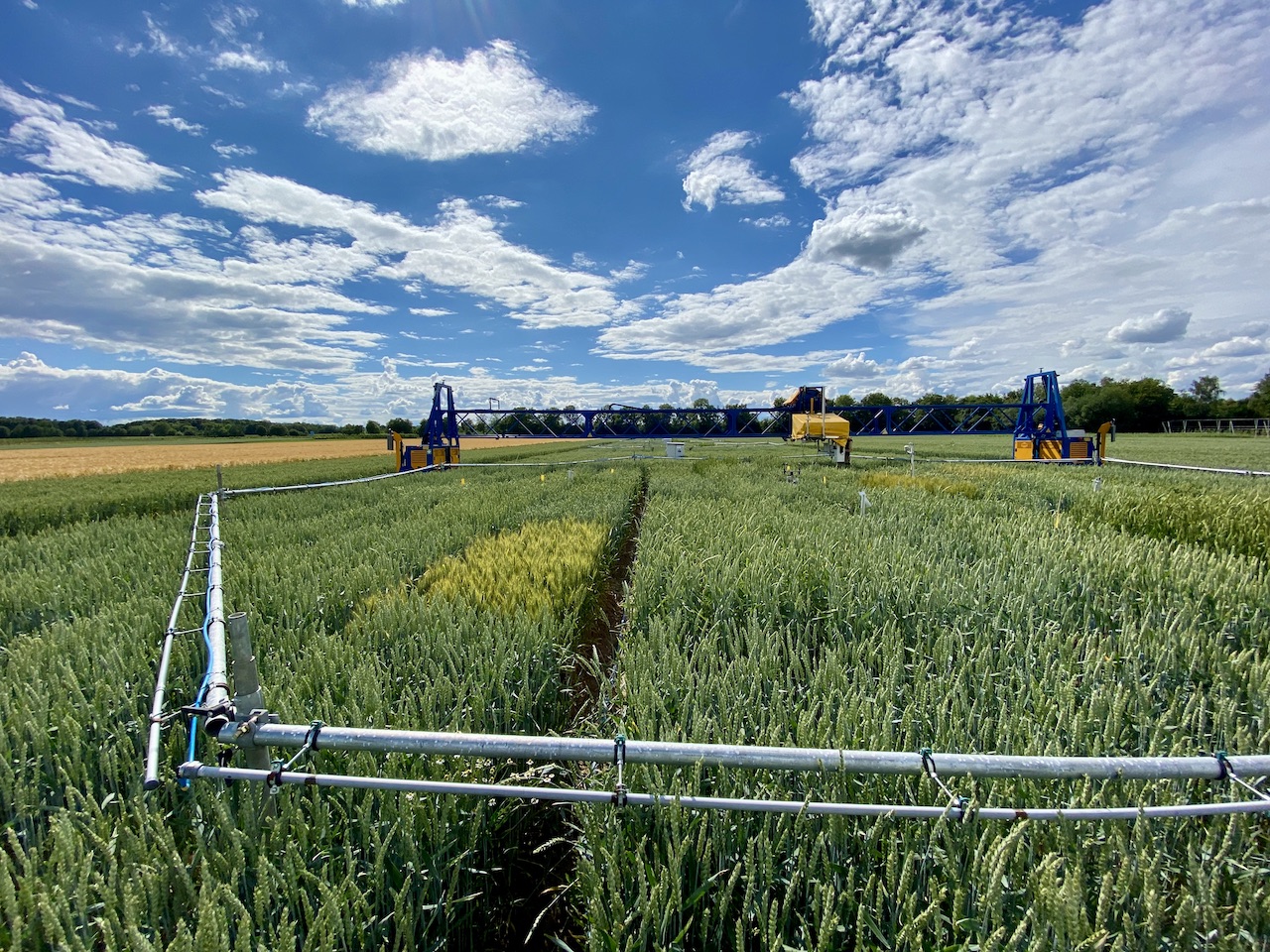

The experimental data consist of the LIFT, PhenoCam, UAV, yield and environmental data from the vegetation period 2020/2021. Abstract: In the context of climate change and global sustainable development goals, future wheat cultivation has to master various challenges at a time, including the rising atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration ([CO2]). To investigate growth and photosynthesis dynamics under the effects of ambient (~434 ppm) and elevated [CO2] (~622 ppm), a Free-Air CO2 Enrichment (FACE) facility was combined with an automated phenotyping platform and an array of sensors. Ten modern winter wheat cultivars (Triticum aestivum L.) were monitored over a vegetation period using a Light-induced Fluorescence Transient (LIFT) sensor, ground-based RGB cameras and a UAV equipped with an RGB and multispectral camera. The LIFT sensor enabled a fast quantification of the photosynthetic performance by measuring the operating efficiency of Photosystem II (Fq'/Fm') and the kinetics of electron transport, i.e. the reoxidation rates Fr1' and Fr2'. Our results suggest that elevated [CO2] significantly increased Fq'/Fm' and plant height during the vegetative growth phase. As the plants transitioned to the senescence phase, a pronounced decline in Fq'/Fm' was observed under elevated [CO2]. This was also reflected in the reoxidation rates Fr1' and Fr2'. A large majority of the cultivars showed a decrease in the harvest index, suggesting a different resource allocation and indicating a potential plateau in yield progression under e[CO2]. Our results indicate that the rise in atmospheric [CO2] has significant effects on the cultivation of winter wheat, with strong manifestation during early and late growth. Article: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2023.1304751/abstract
 PhenoRoam
PhenoRoam