Type of resources
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
-
Sugar beet shoot and root phenotypic plasticity to nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and lime omission

Data were collected in 2019 in Dikopshof, Wesseling, Germany
-
Reflectance orthomosaics of PhenoRob Central Experiment derived from 2021 multispectral image data.
-
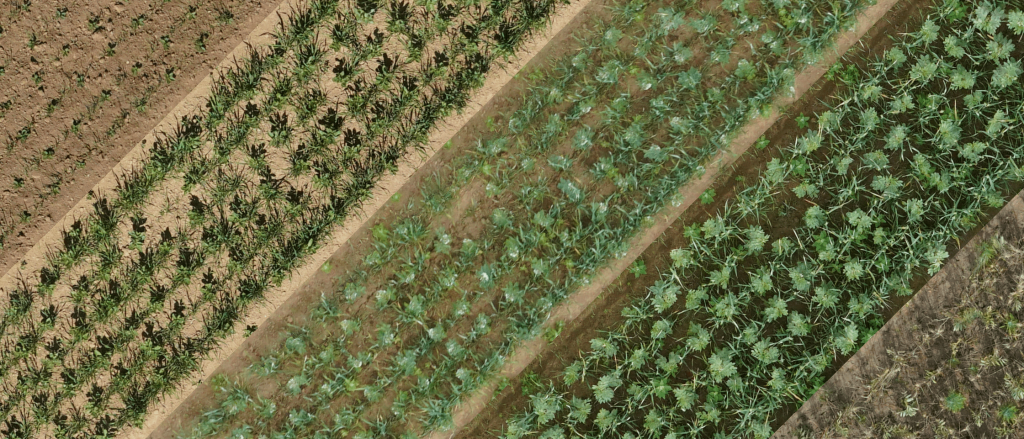

This dataset contains the multitemporal RGB-Image field patches of the "PhenoRob Core Project 5 Mixed Cropping" experiment located at Campus Klein-Altendorf from 2020. 320 Field Patches, including both bean-wheat mixtures but also reference monocultures, were overflown by drone at 11 different time points (RGB) during the growing season. The cropped orthomosaics were rotated for ease of handling and processed to a uniform ground resolution of 3 mm. File endings 'A' and 'B' stand for two different used cameras (also different drones), resulting in slight spectral differences in the images. However, all RGB images are in TIFF format and of type UINT8.
-
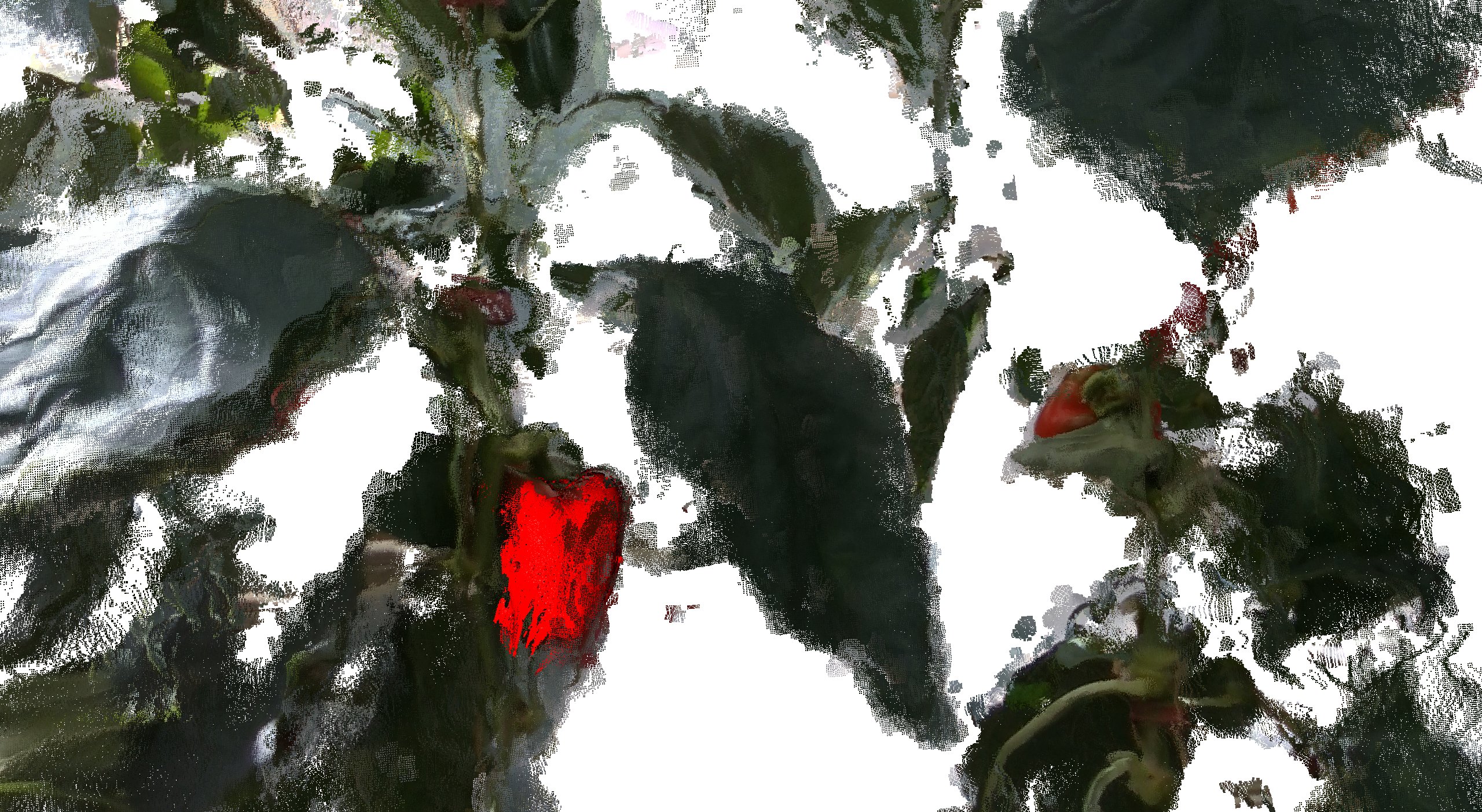

Shape completion dataset for sweet peppers. A detailed description of the dataset can be found in our technical report: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/magistri2024arxiv.pdf We additionally provide a small set of python script to load this data: https://github.com/PRBonn/shape_completion_toolkit
-
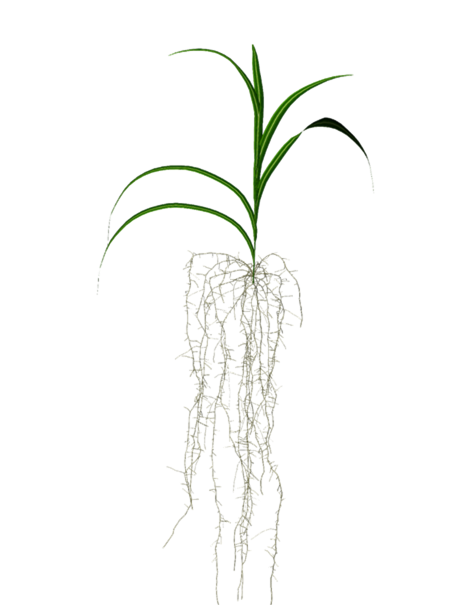
The global supply of phosphorus is decreasing. At the same time, climate change reduces the water availability in most regions of the world. Insights on how decreasing phosphorus availability influences plant architecture is crucial to understand its influence on plant functional properties, such as the root system’s water uptake capacity. In this study we investigated the structural and functional responses of \textit{Zea mays} to varying phosphorus fertilization levels focusing especially on the root system’s conductance. A rhizotron experiment with soils ranging from severe phosphorus deficiency to sufficiency was conducted. We measured architectural parameters of the whole plant and combined them with root hydraulic properties to simulate time-dependent root system conductance of growing plants under different phosphorus levels. We observed changes of the root system architecture, characterized by decreasing crown root elongation and reduced axial root radii with declining phosphorus availability. Modeling revealed that only plants with optimal phosphorus availability sustained a high root system conductance, while all other phosphorus levels led to a significantly lower root system conductance, both under light and severe phosphorus deficiency. We postulate that phosphorus deficiency initially enhances root system function for drought mitigation but eventually reduce biomass and impairs root development and water uptake in prolonged or severe cases of drought. Our results also highlight the fact that root system organization, rather than its total size, is critical to estimate important root functions.
-

A Large Dataset and Benchmarks for Semantic Image Interpretation in the Agricultural Domain. Please find more information at: https://www.phenobench.org/
-

The effect of a mucilage analogue from chia seeds without intrinsic respiratory activity on oxygen diffusion was measured at different water contents during wetting-drying cycles in a diffusion chamber experiment. Artificial soils of various particle size distributions were mixed with various amounts of the mucilage analogue. Additionally, environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) was used to visualize mucilage bridges in the dry soil samples.
-

Data represent an intercropping field experiment carried out at CKA in the year 2021. Shoot and root data collection was conducted with one faba bean cultivar and two spring wheat cultivars sown at three sowing densities. FTIR spectroscopy was used to define the root masses of the two species.
-
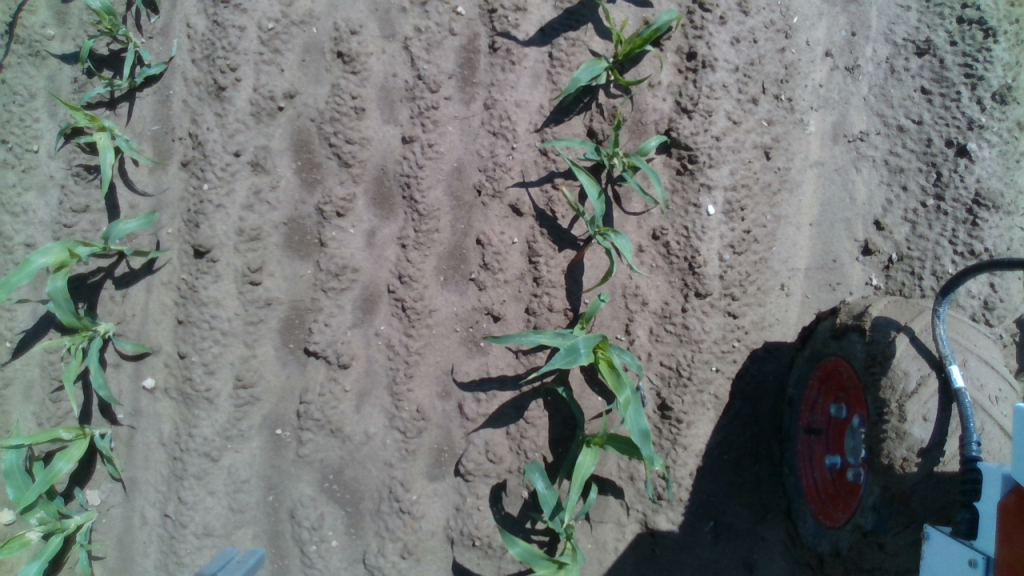

The corn Dataset (CN20) was captured using BonnBot-I. This is a challenging dataset for crop monitoring approaches as it is a grass crop.
-
This data set is generated by the bio-economic farm-level model FarmDyn (https://farmdyn.github.io/documentation/). X_raw.parquet.gzip contains the input data (77 variables), and Y_raw.parquet.gzip contains the corresponding output data (248 output variables). A farm in FarmDyn maximizes its profit based on the what input values are given (e.g. crop prices, farm size, etc.). The output variables are either a farm's decisions of farming activites or the outcomes of its decisions. The data can be read in python by pd.read_parquet.
 PhenoRoam
PhenoRoam